Primary Human Kupffer Cells
Kupffer cells, the resident macrophages of the liver, are the largest population of tissue macrophages in the body. Distributed along the sinusoids of the liver, they play roles in both host defense and tissue homeostasis.
LifeSciences’ Kupffer cells are isolated from whole liver tissue immediately after enzymatic dissociation and enriched prior to cryopreservation.
LifeNet Health is a supplier of MPS-validated hepatocyte and Kupffer cells for use in CN Bio’s PhysioMimix® organ-on-a-chip range of MPS. Reach out to us to learn more.
- Comprehensive donor medical and social history provided
- Histopathology report includes Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) activity score (NAS) along with H&E and Trichrome stained images
- Donor-matched cells and tissue samples
- Cells from healthy and diseased tissue
- Detailed protocols and media recommendations provided
- Access to technical expertise and guidance from LifeSciences’ team of scientists
- Viability ≥70%
- Yield ≥0.5 X 106 cells/vial
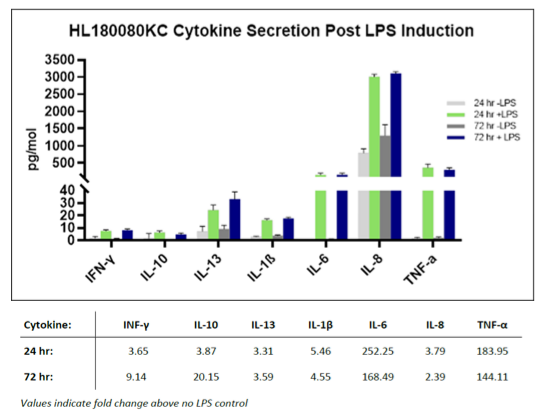
- Cytokine induction by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) stimulation
- Histopathology assessment of tissue of origin by board-certified pathologist; NAS* and fibrosis stage** provided
- Vials of cryopreserved cells shipped and stored at ≤-135°C
*NAFLD (Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease) score (NAS) was assigned according to the standards of the NASH CRN Scoring System (Hepatology 41: 1313-1321, 2005).
**Inflammation and fibrosis were assessed using standard Batts-Ludwig scoring methodology (Scale, 0-4, American Journal of Surgical Pathology 19: 1409-1417, 1995).
Primary Human Kupffer Cells are suitable for multiple applications, including:
- Target identification
- Lead candidate screening
- Preclinical screening and testing
- Liver disease modeling, including Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH)
- Organotypic culture models – Co-cultures, 3D models
- Cell-cell signaling
- Mechanistic studies of Drug-Induced Liver Injury (DILI)
Phagocytosis and inducible cytokine response to pro-inflammatory stimuli such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS) are key functional features of Kupffer cells, a feature that is maintained post isolation.
Comprehensive Portfolio of Liver Cells
200+
Lots
0-6
Nas Scores
0-4
Fibrosis Stages
